Navigation Pane
Uninstall Gitmoxi from ECS Fargate
After you are done testing Gitmoxi you can remove it using terraform destroy.
Go to the gitmoxi-trial directory, which is the directory obtained by unzipping the downloaded package received in email.
cd gitmoxi-trial
cd ecs-fargate
terraform destroy --auto-approve
Uninstall Gitmoxi from EKS
If you installed Gitmoxi on EKS then we will first delete all the Gitmoxi service components from the cluster and then delete the cluster itself.
cd gitmoxi-trial
cd eks
kubectl delete -k install_gitmoxi/
cd create_cluster
terraform destroy --auto-approve
Note make sure to delete any other test applications that you deployed otherwise the terraform destroy will fail because the network interfaces will be in use by the applications pods.
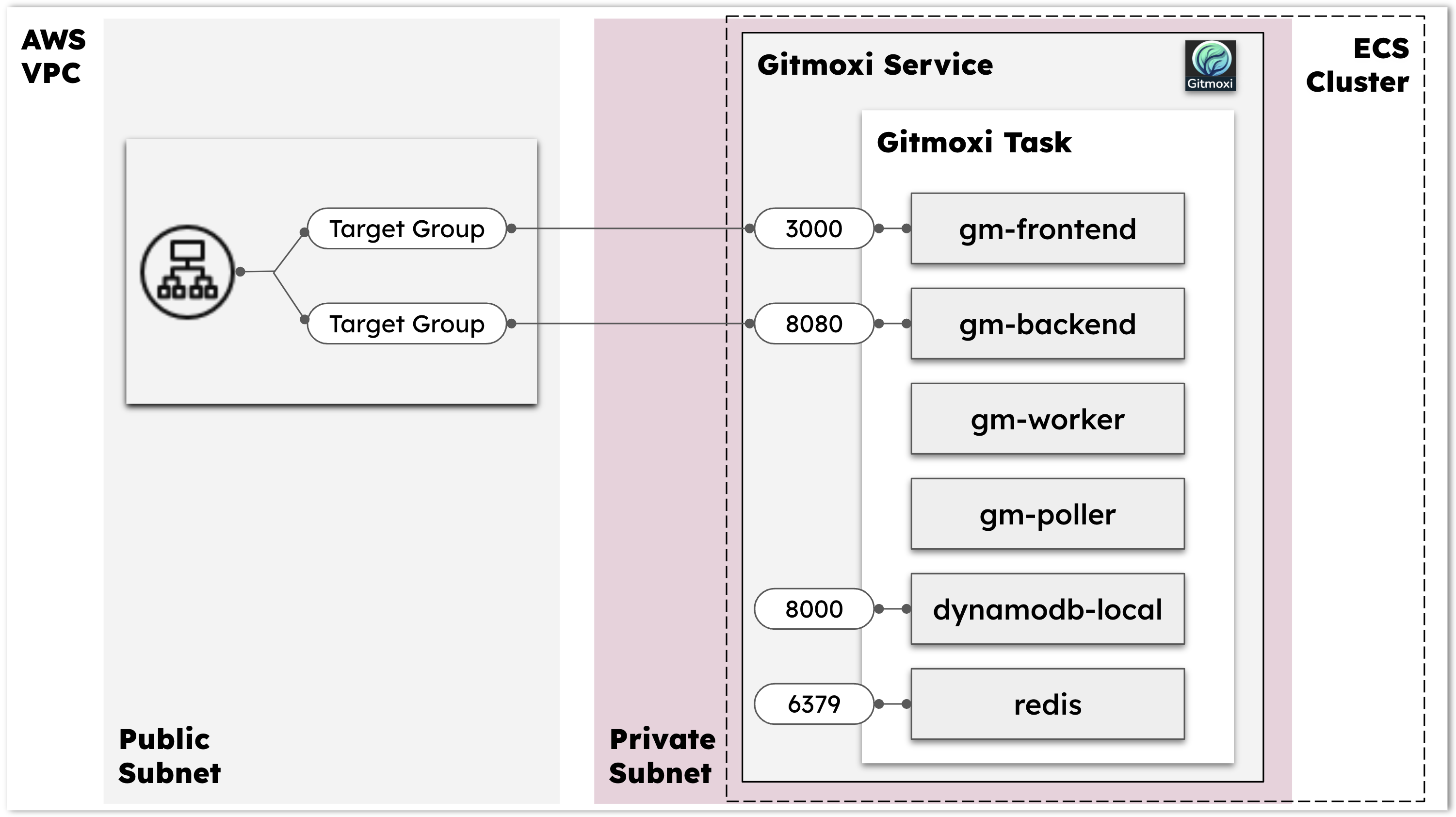
Gitmoxi architecture for trial deployment
For trial, we will deploy all the containers needed for Gitmoxi in a single ECS task (or EKS pod). Below picture captures the overall architecture for the trial deployment that will be created by Terraform. The same architecture applies to EKS as well with ingress controller handling the traffic routing path with ALB.
-
Gitmoxi task: This task consists of 6 containers
gm-frontendmanages the Gitmoxi UI. It serves requests on port 3000 which is exposed via the Application Load Balancer (ALB)gm-backendhandles the API calls It serves requests on port 8080 which is also exposed via the ALB.gm-workeris the main controller logic that handles deployments. It can handle multiple deployments in parallel.gm-pollerprovides ability to listen for GitHub changes and automatically deploy the changes without requiring invocation of Gitmoxi deploy calls. We refer this as thepull(or listening) model.dynamodb-localstores all the Gitmoxi configuration and deployment records. The local dynamodb stores data in memory. So when the task restarts all the data will be lost. For production you will use AWS Dynamodb service instead of local container. Thedynamodb-localserves requests on port 8000 which is accessible only within the private subnet of the VPC.redisis used for thegm-workerfor parallel processing of multiple deployments. It serves request on port 6379 which is also accessible only within the private subnet of the VPC.
The Gitmoxi task is allocated 2vCPU and 4GB of RAM. And the architecture for the containers is ARM64; so it will run on Fargate backed by Graviton instances.
-
Gitmoxi service is a load balanced service which takes two target groups, one for
gm-frontend (port 3000)and another forgm-backend (port 8080).- The service deploys tasks on private subnets
- The security group allows access to the 3000, 8080, 8000, and 6379 required by the Gitmoxi task containers. Only 3000 and 8080 are connected to target groups and accessible from outside the VPC.
-
ALB is used to access the Gitmoxi frontend and backend services. For trial, the listener is connected to port 80. The listener has default forwarding rule to send traffic to the frontend target group which relays request to
gm-frontend. The listener has another rule with higher priority that forwards all traffic on/api/*and/auth/*to the backend target group which relays togm-backend.
IAM rules used
-
Task execution role uses the AWS managed policy
arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AmazonECSTaskExecutionRolePolicywhich grants access to read ECR repositories and to put logs in CloudWatch. -
Gitmoxi task IAM role uses the following AWS managed policies
policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonECS_FullAccessto manage entire lifecycle of ECS service, task, and tasksets.policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AWSLambda_FullAccessto manage entire lifecycle of Lambda functions.policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/ElasticLoadBalancingFullAccessfor reading the ELB listener rules and modifying the traffic weights during blue-green traffic shifting.policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonAPIGatewayAdministratorfor testing Lambda with API-Gatewaypolicy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/CloudWatchReadOnlyAccessto read the CloudWatch alarms.policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccessto deploy Lambda functions
Note that the production deployment has more tighter and specific roles for the Gitmoxi task.
Ready to Simplify Your Deployments?
Join teams who have eliminated deployment complexity with Gitmoxi's GitOps-native approach.
